As of 2022, nearly six out of ten businesses had moved their work to the cloud. This trend is expected to continue in the coming years. (Source: Flexera)
As the cloud computing market expands, so will the demand for individuals with cloud skills. To meet the expectations of the cloud computing job market, the Institute teaches the Cloud Computing course, which introduces the Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud infrastructure as well as Big Data tools like Hadoop, Hive, and Spark. The class is just a starting point, though. Numerous self-paced online resources are available to help develop cloud abilities over time. When I learned Google Cloud Platform (GCP) for the first time, I found it challenging to grasp the large picture of cloud services conceptually, and I could not put what I had learned into practice. As a result, here is some advice that could be useful for cloud computing beginners.
1. Understand the Similarities and Differences Among Each Platform
Current market share can be an indicator when deciding which cloud platform to use. Since 2019, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) have been the top 3 platforms. In Q2 2022, these platforms combined had a 66% share of the worldwide cloud infrastructure services market. While AWS remained the dominator, Azure and GCP are emerging rapidly. Due to the market share, many cloud professionals suggest that beginners start with AWS.
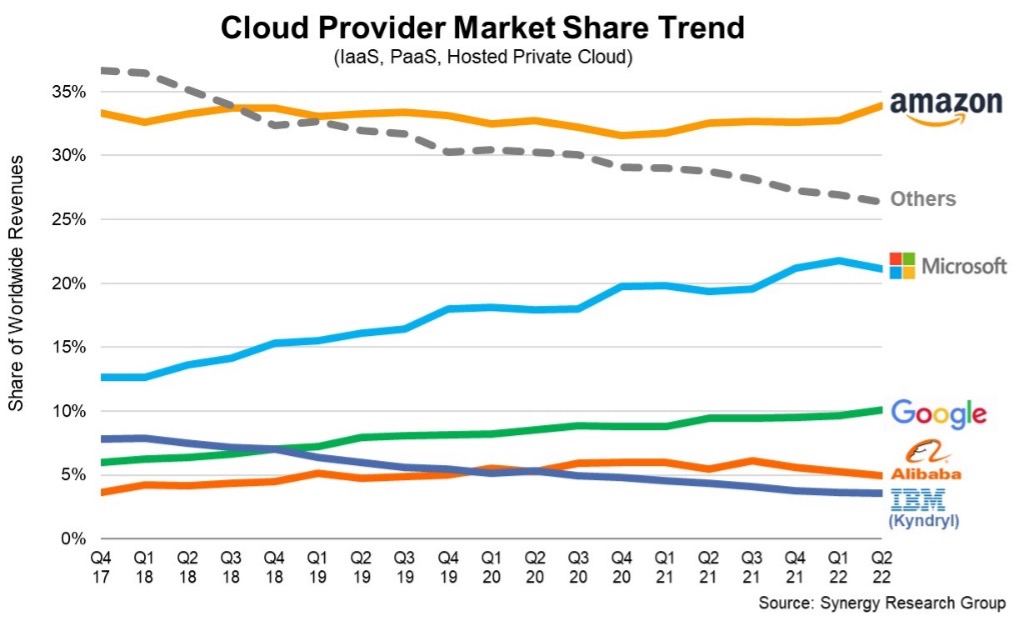
Additionally, each platform has its differentiated strategies. For example, AWS is the first to offer cloud computing services and provides the most affordable prices for large instances. In contrast, Azure bundles services like Microsoft 365, Visual Studio, and GitHub that people already use. Regarding GCP, it contains the most potent Machine Learning (ML) applications and is the cheapest for small instances. Even though they all differ, the fact that various platforms share common infrastructures and services, such as computing, storage, databases, and networking, is a plus. There are courses such as Google Cloud Fundamentals for Azure Professionals or Azure for AWS professionals that help you adapt to another platform. Thus, you could select a learning platform that best fits your learning style, because transferring your knowledge from one platform to another wouldn’t be too difficult.
2. Identify Job Role and Choose a Learning Path
Cloud computing is a broad concept with numerous job functions that use various cloud services. First-time users should define their job role first and then focus on tools that are relevant to that position. For different professionals, cloud platforms offer a variety of learning paths and certifications. From my experience, some cloud concepts or infrastructures intended for developers or engineers are optional for data professionals because they could go straight into paths like data engineers, data analysts, or data scientists to use their analytical abilities. Here is a brief introduction to common learning paths from which data professionals could start.
a. Basic Cloud Concepts
Understanding general cloud concepts could help those without a background in computer science to gain a comprehensive understanding of cloud computing terms before digging deeper into cloud services and infrastructures. For these people, the AWS Cloud Practitioner Essentials course explains its services with simple examples. GCP also has a Cloud Digital Leader learning path designed to increase the understanding of cloud-related terminologies.
b. Cloud Fundamentals/Cloud Practitioner
Those familiar with cloud concepts who want to learn cloud infrastructures and commonly used services of a specific platform can consider taking cloud fundamental courses. These courses are designed to help individuals who are new to cloud technology and seek an overall understanding of the cloud. The digital training introduces important cloud concepts, services, computing and storage, security, architecture, pricing, along with important resources and policy management tools. If you are interested in getting your first cloud certification, you could look at the comparison of official learning resources in the next section to find a course that meets your learning habits.
c. Data Engineers/Databases
Data engineers integrate, transform, and consolidate data from various structured and unstructured data systems into structures suitable for building analytics solutions. They ensure that data pipelines and storage are high-performing, efficient, organized, and reliable. They also design, implement, monitor, and optimize data platforms to meet the data pipeline needs. Learners would work on tools such as data pipelines, Synapse Analytics, DataBricks, data lakes, data warehouse, stream analytics, Azure Blob storage, MongoDB, SQL Server, Amazon RDS, Amazon Keyspaces, and Amazon ElastiCache in this learning path.
d. Data Analysts/Data Analytics
A data analyst collects and analyzes data to identify trends and develops valuable insights to help solve problems and inform business decisions. They are proficient in data cleansing, visualization, designing, creating, and deploying data analytics solutions, integrating with IT infrastructure, and applying development lifecycle practices. They also advise on data governance and configuration settings for administration, monitor data usage, and optimize the performance of the data analytics solutions. Typical tools in this learning path include visualization tools like Power BI, Quicksight, or Looker, databases tools like BigQuery or Redshift, synapse analytics, and stream analytics.
e. Data Scientists/Machine Learning
Data scientists’ path teaches professionals who “design, build, productionize, optimize, operate, and maintain ML systems” (Google Cloud training) to learn how to integrate ML and artificial intelligence (AI) into tools and applications. Responsibilities for this role include
- designing and creating a suitable working environment for data science workloads
- exploring data
- training machine learning models
- implementing pipelines
- running jobs to prepare for production
- managing, deploying, and monitoring scalable machine learning solutions.
Tensorflow, computer vision, natural language processing, Databricks, 5G, and autonomous AI are some examples of the applications.
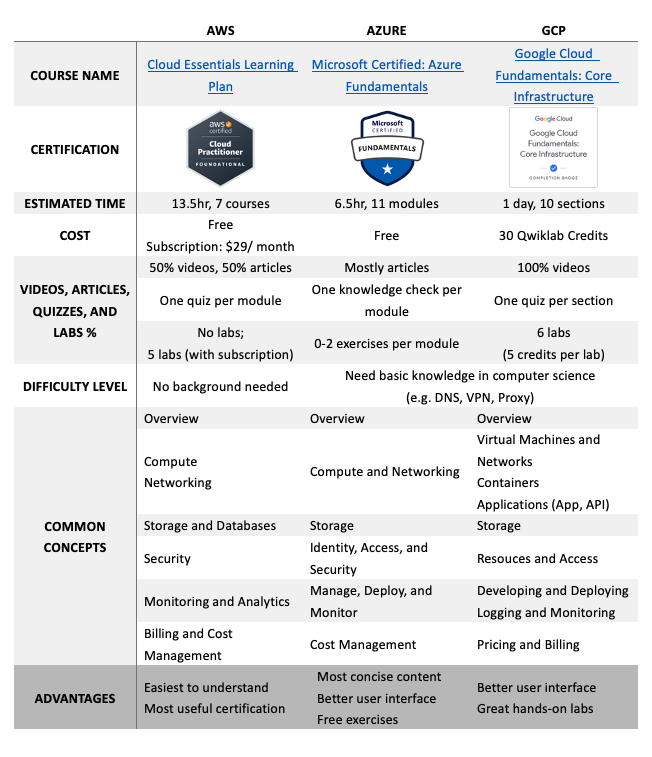
3. Comparison Between Official Learning Resources
4. Other Free Learning Resources
Aside from courses on the official learning platforms, third-party self-learning platforms such as Udacity and Coursera sometimes will cooperate with cloud service providers to provide scholarship programs and promotions free for a limited time.
For students interested in playing around in the cloud environment,
- AWS Educate offers hundreds of hours of free training and hands-on labs.
- Azure has $100 credit to try free services on Azure.
- GCP gives 200 free Google Cloud Skills Boost credits to access free online labs, quests, and courses on Qwiklabs.
You could also consider AWS 1-year free tier, Azure 12-month free services, or GCP $300 free credits. Be sure to understand what services are included in the free tier, how much service usage you can get, and understand the costs of using cloud services. Also, remember to close up all services after you are done to avoid additional charges.
Lastly, cloud providers often host 1-3 days of training, workshops with specific topics, timely challenges such as Halloween or Earth Day challenges, etc., for free. These events sometimes even give away exam coupons or swag for those who join. Since these events are announced irregularly, I recommended signing up for their emails and following their social media to get the latest updates.
In conclusion, those with little or no technical background could start by learning basic cloud concepts. Individuals familiar with conventional computing infrastructure should consider concentrating on one platform that best suits their requirements. Data professionals could join the specialty program or learn particular applications straightaway. Furthermore, trying out some lab practices is definitely worthwhile. As the cloud market grows, it is never too late to learn cloud computing!
References
Q2 Cloud Market Grows by 29% Despite Strong Currency Headwinds; Amazon Increases Its Share
Cloud Computing Careers and Certifications: First Steps
Columnist: Yvonne Tsai
